The major world religion Islam, that was the second largest religion after Christianity, introduced by the Prophet Muhammad in 7th century CE in Arabia that had a relation with both Mesopotamia and Egypt. As in Constantine’s Christianity/ Byzantine, Islamic culture also mostly focus on the religion. Thus, the highest and most effective expression of the Islam was the religious architecture such as madrasah and mosques that were the center of Islamic culture. Apart from its own style and language, Islamic architecture include also various forms and styles of other countries. We may say that, the character of architecture also somehow related with the Mediterranean culture.
The most essential and significant structures were mosques that was the gathering place to worship, also a discussion and resting place. It is defined by some distinctive elements. Such as, minaret, mihrab, dome, courtyard etc. The minaret that is like a slender tower, is one of the oldest elements of Islamic architecture. It was like a reminder of the entity of Islam.
Mecca is the city that Muhammad was born, also a holy and pilgrimage (site) for nomadic tribes of Arabia. It hosted many mosques, tombs, forts that were create a circular orientation. Besides, Mecca is the home of the Kaaba that is the most important Islamic mausoleum. This pre-islamic monument that has a meaning ‘cube’ but not properly a cube, built from granite and covered with a black fabric to protect the Kaaba. The pilgrims come together at the surrounding courtyard (haram).


Apart from the Mecca, Muhammad moved to Medina to build up the first Islamic city. He encourage the modest architecture because of taking the afterlife as a base. Unlike from the pagan temple’s style, first Muslims preferred the secular structures. With an order of Muhammad, an enclosure was built, known as the prophet Muhammad’s house with a square courtyard (Mosque of the Muhammad) that was a primitive structure. It considered as the first mosque in Medina. At first, for Muslims praying, the direction of the worship, qibla faced with Jerusalem, but after the conquest of the Medina, it become Kaaba.


-The first mosques included some basic elements such as, fountains and covered halls.
Since the 7th century, the mosques have built around the world with its various types. While there are various types, three common plans can be defined. One of was the hypostyle hall that adjoin with an open courtyard (sahn), was the main characteristic of the hypostyle mosque which dates back to end of the 7th century. We come across with one of the earliest example in Kufah, Iraq, with a square hall and spaced columns. Kufah was the new city that Arabs founded, was established on a grid with crossed streets like the ancient Rome, include some open plazas (maydan) that surrounded by orthogonal streets.

Diagram reconstruction of the Prophet’s House, Medina

The Umayyad Period: Jerusalem and Damascus
After the Muhammad’s cousin Ali took the power, moved the capital from Mecca to Kufah. Then the tribe of Umayyad that were rival, settled in Damascus. The caliph of Umayyad, built the Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem in the late 7th century, that was the oldest Islamic most visible monument, built over the rock. The root of the mosaics and structure of the dome came from Byzantine style. It located near the center of Temple Mount with a central plan that covered by a central dome like the Christians martyrium. The octagonal arcade( that had pointed arch or ablaq features)surrounding the rock. Besides, we still can see continuation of use of mosaics. Both exterior and interior decorated with marbles and mosaics.
After the Umayyads gained strength over the Mecca, they started to build much more fascinating mosques. One of was enlarged Mosque of the Prophet and other one was Al-Aqsa Mosque that was in the Jerusalem Old Temple Mount, had a basilical hypostyle hall. (Similar with the Christian Basilica) They contained one of the essential elements of mosques that is mihrab. It is a hollow in the wall and specify the qibla. Near the mihrab there was an enclosure, a box that called maqsurah to preserve the ruler. Besides, next to the mihrab there was minbar is a covered pulpit that located on a qibla wall.
The other essential monument was Great Mosque. It contains prayer hall and large courtyard that enclosed an octagonal pavilion, surrounded with the arcades supported by Corinthian columns. The walls of mosque covered with mosaics.
On the other hand the Damascus’s desert palaces that served as caravansaries were center of the agricultural property. These palaces had solid walls as symbolic. Qasr Mshatta can be an example that we can see the both Roman and Sassanid influences. It had limestone walls, symmetrical plan, central entry hall and larger court.

In the middle of the eight century, the revolution of Abbasid ended the Umayyad dynasty and established a round city with a capital called Baghdad (Madinah el-Salam (city of peace)). The initial plan would be a perfect circle with the southwest gate that pointed the Mecca. The entries had vault arches that also called iwan and hall with a golden dome. Besides, Baghdad had cross-longitudinal streets that covered with vaults. On the other hand, imperial palaces that framed by the central void, started to be constructed. Besides, the houses for caliph’s family were in the outer of the round and the administrative buildings located the inside of the round.
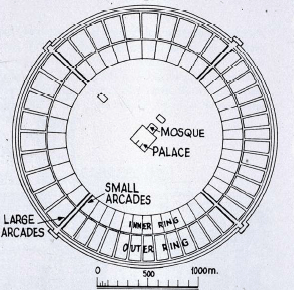
Baghdad Round City
A decade later Harun transferred the capital to Ar-Raqqah and began to construction of octagonal buildings. After the death of Harun, Samarra became the capital with extended Abbasid palaces and mosques. Caliph’s Palace was an example of it. The gateway formed by the iwans. The ground included amphitheater, central esplanade and gardens. Then, when Mutawakkil started to administer the city, he wanted to build most largest mosque in the world. So that, the Great Mosque of Samarra emerged. It has a rectangular layout and the courtyard surrounded by arcades. Besides, its’ minaret – Malwiya Tower- was a cone with spiral ramp.

Great Mosque of Samarra
Additionally, in Tunusia the dynasty of Aghlabid, Great Mosque of Kairouan was rebuilt with a high minaret, as an imitation of Great Mosque of Baghdad.



